In the rapidly evolving world of healthcare, digital health and telemedicine stand out as pivotal innovations, fundamentally shifting how you access and receive medical services.
We’re going to delve into the transformative impact of these technologies, exploring their role in enhancing patient care, increasing accessibility, and optimizing healthcare delivery.
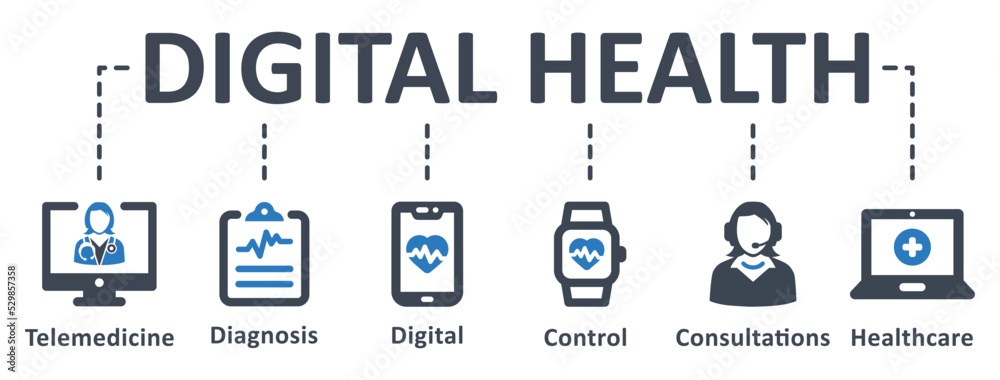
Understanding Digital Health and Telemedicine
Digital health encompasses a wide range of technology-based tools aimed at improving your health and wellness. It includes everything from wearable fitness trackers to advanced diagnostic software.
Telemedicine is a subset of digital health, focusing specifically on the delivery of healthcare services remotely.
You can think of telemedicine as using technology to bring the doctor to you, enabling medical consultations through video calls, phone calls, or chat.
Together, digital health and telemedicine create a more connected, accessible, and efficient healthcare experience for you.
Historical Evolution
Digital health and telemedicine have come a long way, evolving significantly over the years.
- Starting in the late 20th century, early forms of telemedicine involved phone-based consultations.
- The development of the internet in the 1990s paved the way for more advanced telemedicine services, such as video conferencing, telemedicine websites, and remote monitoring.
- The introduction of smartphones and wearable devices in the 2000s further expanded the capabilities of digital health, making it easier for you to track your health data and communicate with healthcare providers.
- Today, telehealth and telemedicine are integral parts of the healthcare system, constantly evolving with the advent of new technologies. There are entire telemedicine companies like Esanjeevani.
You can find different types of telemedicine. Real-time telemedicine enables you to have a live interaction with healthcare professionals through video calls or phone.
Store-and-forward telemedicine allows you to send your medical information to a healthcare provider at a convenient time, while remote patient monitoring lets track your health data through devices.
Key Technologies Involved
Digital health and telemedicine rely on a variety of key technologies to function effectively. These include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital versions of patients’ paper charts, making it easier for healthcare providers to track and share patient information.
- Mobile Health Apps: Apps that offer health-related services on smartphones, allowing you to monitor your health and communicate with healthcare providers for telemedication.
- Video Conferencing Tools: Software that enables virtual consultations between you and healthcare providers.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Devices that collect health data from you and transmit it to healthcare providers for assessment.
- Cloud Computing: Technologies that store and manage vast amounts of health data securely, facilitating easy access and sharing.
- Artificial Intelligence: Algorithms that analyze health data to assist with diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient engagement.
- Secure Messaging Platforms: Tools that allow secure communication between you and healthcare providers.
- Interoperability Solutions: Technologies that ensure different digital health tools and systems can work together seamlessly.
- Virtual Reality: Used for patient education, pain management, and therapy.

Benefits for Patients
Digital health and telemedicine offer numerous benefits for you as a patient, including:
- Accessibility: Get medical advice from anywhere, especially useful if you live in a remote area or have mobility issues.
- Convenience: Schedule appointments and consult with healthcare providers without the need for travel.
- Time-saving: Reduce time spent in waiting rooms and traveling to appointments.
- Cost-effectiveness: Save on travel costs and sometimes even on the cost of consultations with free telehealth without insurance.
- Improved Communication: Telehealth services share information with your healthcare provider and receive quicker responses.
- Personalized Care: Access tailored health programs and advice based on your health data.
- Enhanced Privacy: Conduct consultations privately from your home.
- Access to Specialists: Consult with specialized doctors who might not be available locally.
- Support and Education: Access educational materials and support groups easily.
These benefits contribute to a more convenient, accessible, and personalized virtual healthcare experience.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers
For healthcare providers, digital health and telemedicine offer significant advantages, including:
- Efficient Patient Management: Streamline appointments, easily access patient records, and reduce no-shows.
- Broader Reach: Treat patients from various locations, expanding your practice.
- Cost Reduction: Online telemedicine saves on overhead costs associated with in-person appointments.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Keep patients more engaged in their healthcare journey, leading to better outcomes.
- Access to Patient Data: Easily access and share patient health data for more informed decisions.
- Enhanced Communication: Communicate with patients and other healthcare providers efficiently.
- Time-saving: Reduce time spent on administrative tasks, focusing more on patient care.
- Flexible Work Environment: Have the option to provide consultations from various locations.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with patient data and health trends, aiding in professional development.
- Support for Preventive Care: Monitor patient health data continuously, allowing for preventive care measures.
These benefits lead to a more efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered healthcare practice.
Ethical Considerations
In digital health and telemedicine, ethical considerations are crucial to ensure patient rights and safety. Key considerations include:
- Patient Privacy: The use of telemedicine in healthcare must protect patient data rigorously to prevent unauthorized access and breaches.
- Informed Consent: Ensure patients fully understand and agree to the use of digital tools and remote consultations.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to safeguard patient information.
- Access Equity: Work to provide digital health services to all, regardless of location or socio-economic status.
- Transparency: Be clear about how patient data is used and stored.
- Quality of Care: Maintain high standards of care, ensuring that remote consultations do not compromise quality.
- Professional Boundaries: Establish and maintain appropriate boundaries in virtual patient interactions.
- Accountability: Be accountable for the advice and diagnoses provided through digital health platforms.
- Patient Autonomy: Respect patient choices and provide the necessary information for informed decision-making.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly update and monitor digital health tools to ensure they are functioning properly and providing accurate information.
Conclusion
Digital health and telemedicine are transformative forces in healthcare, breaking down barriers to access and bringing a host of benefits to both patients and healthcare providers.
Despite the clear advantages, it’s vital to navigate ethical considerations such as patient privacy, data security, and equitable access to ensure a safe and trustful environment.
Embracing these innovations while upholding ethical standards will continue to shape the future of healthcare, making it more accessible, personalized, and efficient.